
Gum surgery, also known as periodontal surgery, is a specialized dental procedure designed to address a range of gum-related issues, from gum disease to cosmetic concerns. The health of your gums is crucial to the overall well-being of your teeth and smile, and in some cases, surgery may be needed to restore or enhance your gum health. Gum surgery can treat conditions like gum disease (periodontitis), gum recession, or uneven gum lines, and it can also help with cosmetic concerns such as a gummy smile or excessive gum tissue.
While gum surgery might sound intimidating, it is a common and highly effective procedure that can lead to healthier gums, stronger teeth, and an improved smile. With advancements in modern dentistry, many types of gum surgery are minimally invasive and offer quick recovery times, allowing patients to return to their normal activities with minimal discomfort. Whether you need surgery to treat periodontal disease, correct gum recession, or enhance the aesthetics of your smile, gum surgery can provide a lasting solution.
In this guide, we will explore everything you need to know about gum surgery, including the different types of procedures, when they are necessary, the recovery process, and the benefits of choosing gum surgery to improve your oral health and appearance.
frequently asked questions
What is gum surgery?
Gum surgery refers to any surgical procedure that is performed on the gums to address health issues or cosmetic concerns. The most common reasons for gum surgery include treating gum disease, correcting gum recession, reshaping the gums for cosmetic purposes, or treating problems with the bone supporting the teeth. Some of the most common types of gum surgery include gum grafting, pocket reduction surgery, crown lengthening, and gum contouring.
When is gum surgery necessary?
Gum surgery may be recommended for various reasons, such as: Severe gum disease (periodontitis) that hasn’t responded to nonsurgical treatments like scaling and root planing. Gum recession that exposes tooth roots and leads to sensitivity or increased risk of decay. Excessive gum tissue (gummy smile) that makes your teeth look smaller or uneven. Bone loss around teeth due to advanced gum disease that requires bone grafts or regeneration. Cosmetic purposes to reshape or even out the gum line for a more aesthetically pleasing smile. Your dentist or periodontist will evaluate your situation and determine whether surgery is the best option for you.
What types of gum surgery are there?
There are several types of gum surgery, each designed to address specific issues: Gum Grafting (Gum Graft Surgery): This procedure involves taking tissue from another part of your mouth (often the roof of your mouth) or using a donor graft to cover exposed tooth roots caused by gum recession. Pocket Reduction Surgery (Flap Surgery): This is often used to treat advanced gum disease. The gums are lifted away from the teeth to allow for deep cleaning of the roots, and then the gums are repositioned or reshaped to fit snugly around the teeth. Crown Lengthening: This surgery removes excess gum tissue to expose more of the tooth, often done to correct a "gummy smile" or when a tooth is too short to be properly restored with a crown. Bone Grafting: If gum disease has caused bone loss around a tooth, a bone graft may be performed to restore the lost bone and support the tooth. Laser Gum Surgery: A minimally invasive option that uses laser technology to remove infected tissue and reshape the gums, reducing recovery time and discomfort.
Is gum surgery painful?
Most gum surgeries are performed under local anesthesia, so you should not feel pain during the procedure. For more extensive surgeries, such as those involving multiple areas of the gums, sedation may be used to help you relax. After the anesthesia wears off, mild to moderate discomfort may occur, but this can typically be managed with pain relievers prescribed by your dentist or periodontist. For most patients, the pain is temporary and subsides within a few days.
How long does gum surgery take?
The duration of gum surgery varies depending on the complexity of the procedure. Simple procedures like crown lengthening or minor gum grafting may take 1 to 2 hours, while more extensive surgeries, such as pocket reduction or bone grafting, may take longer. Your dentist or periodontist will give you a more accurate time estimate based on your specific needs.
What is the recovery time for gum surgery?
Recovery times vary depending on the type of surgery performed and the extent of the procedure. Generally, you can expect: Mild swelling and discomfort for the first few days. Soft food diet for a few days to weeks after the procedure to avoid irritating the surgical site. Avoidance of strenuous physical activity for about 1-2 weeks. Follow-up appointments to monitor healing and remove sutures, if necessary. Most patients return to normal activities within a week or two, but it can take several weeks for the gums to fully heal. Your periodontist will provide personalized post-surgical care instructions to ensure optimal healing.
Are there any risks associated with gum surgery?
While gum surgery is generally safe, there are some risks to be aware of, including: Infection: If proper care is not taken after surgery, there is a risk of infection at the surgical site. Excessive bleeding: This is rare, but some bleeding can occur after the surgery. Gum or bone loss: In some cases, the surgery may not fully restore the gums or bone to their original condition, and further treatment may be necessary. Scarring: Depending on the extent of the procedure, there may be some scarring, though this is usually minimal and fades over time. Your periodontist will work with you to minimize these risks and ensure the best outcome.
How should I care for my gums after surgery?
Proper aftercare is essential for a successful recovery. You’ll likely be advised to: Avoid hard or crunchy foods that could irritate the surgical site. Keep your mouth clean by gently brushing your teeth and gums, avoiding the surgical area for the first few days. Use salt water rinses or an antimicrobial mouthwash to keep the surgical area clean. Take prescribed antibiotics if necessary to prevent infection. Attend follow-up appointments to monitor healing and ensure the gums are recovering as expected. Your periodontist will provide you with detailed instructions on how to care for your mouth and ensure a smooth recovery.
How much does gum surgery cost?
The cost of gum surgery varies depending on the procedure and your location. On average, gum grafting can cost between $600 and $3,000 per site, while more complex procedures like bone grafting or pocket reduction surgery may cost more. Many dental insurance plans cover part of the cost of gum surgery, especially if it’s medically necessary to treat gum disease. Be sure to check with your insurance provider to understand your coverage.
Will I need gum surgery more than once?
In most cases, gum surgery is a one-time treatment. However, if you’re undergoing surgery to treat gum disease, ongoing maintenance may be necessary, such as regular cleanings or periodontal care. For cosmetic procedures, the results are generally permanent, though factors like aging or gum disease can affect the long-term outcome. Your periodontist will discuss long-term care options to help maintain your results.
Conclusion
Gallery
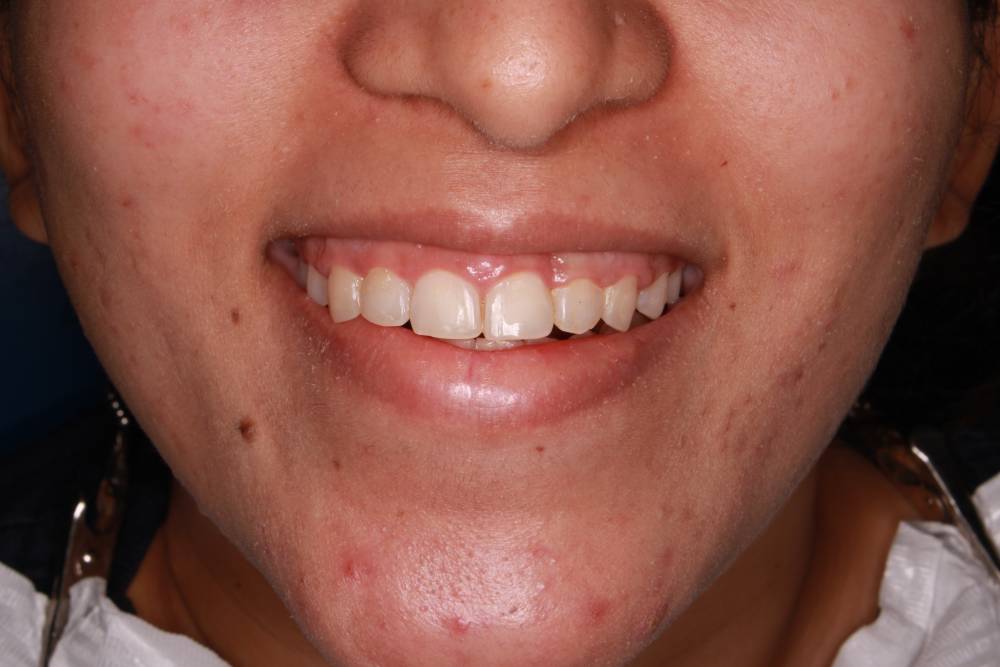
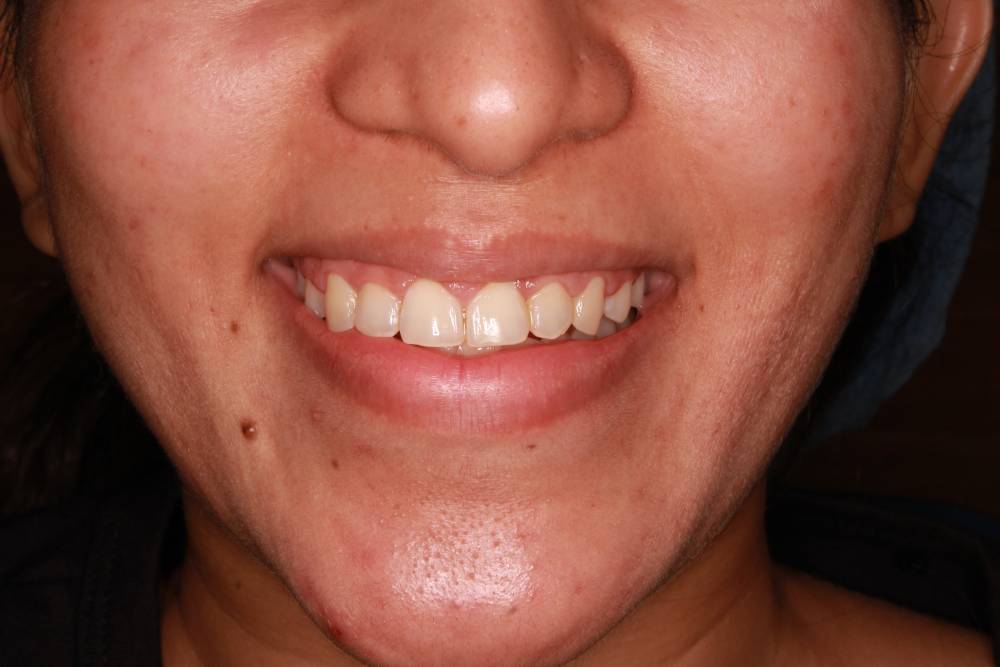
Gum Surgery
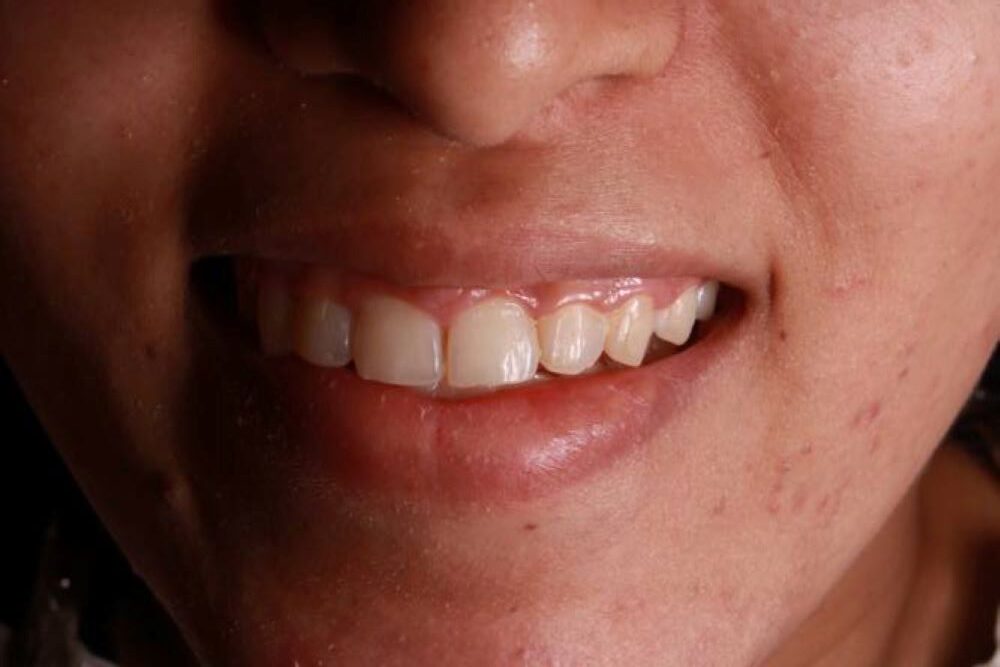
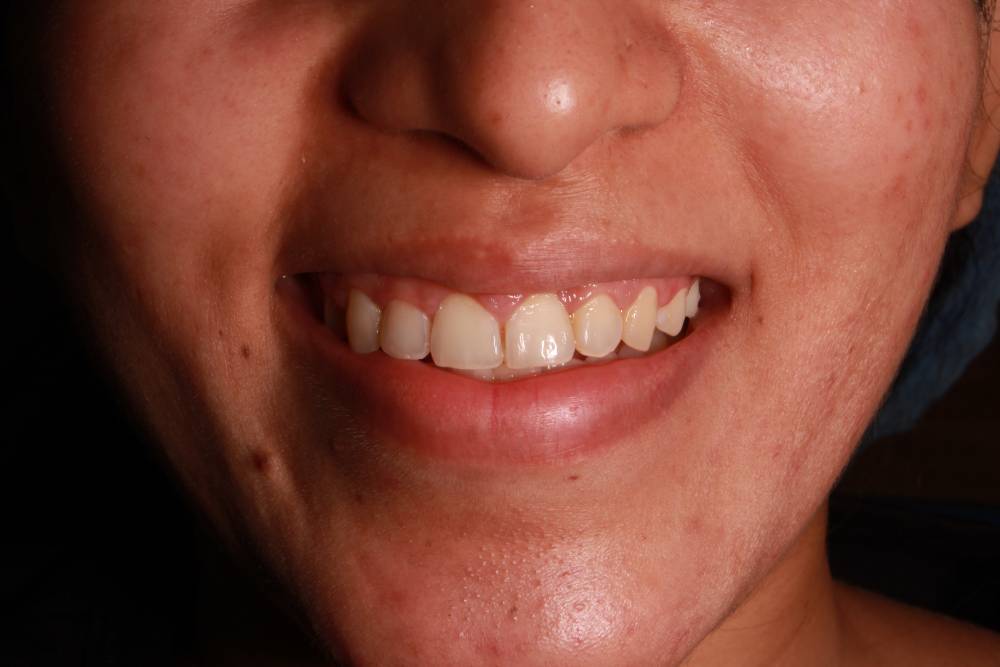
Gum Surgery

Before

After

Before

